1. Design and analysis of VRCA64
Source edi.sh and synopsys.sh to run EDI and PrimeTime.
Go to directory 3-as in the top-level directory.
Go to directory VRCA64. The files in this directory are the same as those used in the tutorial.
We used 0.6 (60%) for the initial utilization in the tutorial. Redesign the layout using 0.4 for the initial utilization.
What to submit
Timing reports (obtained by running "report_timing") after placement, CTS, routing, and postRoute optimization.

A final timing report obtained by PrimeTime.

2. Design and analysis of VCLA256
This design is a 256-bit carry-lookahead adder.
Go to directory 3-as/VCLA256.
Design a layout of VCLA256. Use the following settings.
Utilization: 0.6
Core to left, right, top, bottom: 5.0
Skip "CTS" and "post-CTS optimization" becase this design is purely-combinational.
What to submit
Timing reports (obtained by running "report_timing") after placement, pre-CTS optimization, routing, and postRoute optimization.
A screen-shot of the final layout (after post-route optimization).
A final timing report obtained by PrimeTime.
3. Wirelength vs. utilization
Redesign VCLA256 using five different utilization values (0.5, 0.55, 0.6, 0.65, and 0.7). (you design five different layouts)
You can find the final wirelength in the log.
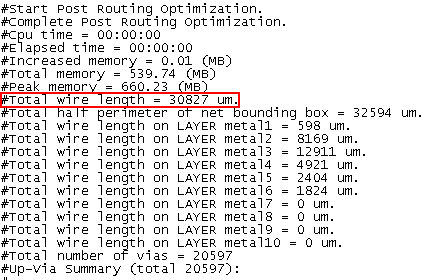
Plot a graph whose x-axis and y-axis are the utilization and the final wirelength, respectively.
Do you see any trend in the graph?
What to submit
The utilization-wirelength plot.
Discussion on the relationship between the final wirelength and the utilizaiton.


